模拟退火算法
模拟退火算法最早的思想由Metropolis 等( 1953 )提出, 1983 年 Kirkpatrick 等将其应用于组合优化。
算法的目的:
克服优化过程陷入局部极小;
克服初值依赖性。
物理退火过程
在物理学中,退火是将金属加热到极高温度,然后让其极其缓慢地冷却的过程。
- 高温状态:原子运动剧烈,处于无序状态(高能量)。
- 等温过程 对于与环境换热而温度不变的封闭系统,系统状态的自发变化总是朝自由能减少的方向进行,当自由能达到最小时,系统达到平衡态;
- 缓慢冷却:原子逐渐找到最稳定的位置,形成整齐的晶体结构。
- 最终状态:系统的内能最低(全局最优)。
如果冷却得太快(淬火,Quenching),原子来不及调整位置就被“冻结”在杂乱的状态,系统处于亚稳态(局部最优,内能较高,材料脆)。
温度越低,物体的能量状态越低,到达足够的低点时,液体开始冷凝与结晶,在结晶状态时,系统的能量状态最低。缓慢降温(退火时,可达到最低能量状态;但如果快速降温(淬火,会导致不是最低能态的非晶形。
Boltzmann概率分布
在温度T,分子停留在状态r满足Boltzmann概率分布

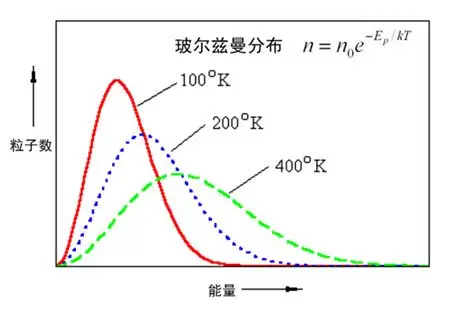
在同一个温度T,选定两个能量E1 auto solve( const State& initial_state, EnergyFunc energy_func, Params params = Params{}, NeighborFunc neighbor = NeighborFunc{}, CoolingPolicy cooling = CoolingPolicy{}, ConstraintPolicy constraint = ConstraintPolicy{} ) { using AcceptancePolicy = MetropolisAcceptance; detail::Solver solver(params, energy_func, neighbor, cooling, AcceptancePolicy{}, constraint); return solver.solve(initial_state); }} // namespace sa#endif // SA_SA_HPP[/code]policies.hpp- #ifndef SA_SA_HPP
- #define SA_SA_HPP
- #include "params.hpp"
- #include "policies.hpp"
- #include "detail/solver.hpp"
- namespace sa {
- /**
- * @brief 模拟退火通用求解函数
- * * @tparam State 状态类型 (自动推导)
- * @tparam EnergyFunc 能量函数类型 (自动推导)
- * @tparam NeighborFunc 邻域函数类型 (可选)
- * @tparam CoolingPolicy 降温策略 (可选)
- * @tparam ConstraintPolicy 约束策略 (可选)
- * * @param initial_state 初始状态值
- * @param energy_func 能量函数句柄
- * @param params 算法参数配置
- * @param neighbor 邻域生成器实例
- * @param cooling 降温器实例
- * @param constraint 约束器实例
- * @return std::pair<State, double> {最优状态, 最优能量值}
- */
- template<
- typename State,
- typename EnergyFunc,
- typename NeighborFunc = DefaultNeighbor<State>,
- typename CoolingPolicy = ExponentialCooling,
- typename ConstraintPolicy = std::nullptr_t
- >
- auto solve(
- const State& initial_state,
- EnergyFunc energy_func,
- Params params = Params{},
- NeighborFunc neighbor = NeighborFunc{},
- CoolingPolicy cooling = CoolingPolicy{},
- ConstraintPolicy constraint = ConstraintPolicy{}
- ) {
- using AcceptancePolicy = MetropolisAcceptance;
- detail::Solver<State, EnergyFunc, NeighborFunc, CoolingPolicy, AcceptancePolicy, ConstraintPolicy>
- solver(params, energy_func, neighbor, cooling, AcceptancePolicy{}, constraint);
- return solver.solve(initial_state);
- }
- } // namespace sa
- #endif // SA_SA_HPP
- #ifndef SA_POLICIES_HPP
- #define SA_POLICIES_HPP
- #include "params.hpp"
- #include "detail/traits.hpp"
- #include <cmath>
- #include <random>
- #include
- #include <stdexcept>
- #include <vector>
- namespace sa {
- // 默认降温策略
- struct ExponentialCooling {
- inline double operator()(double T, const Params& p) const noexcept {
- return T * p.alpha;
- }
- };
- // 默认接受策略 (Metropolis 准则)
- struct MetropolisAcceptance {
- template<typename RNG>
- bool operator()(double delta_E,
- double T,
- RNG& rng,
- std::uniform_real_distribution<double>& dist) const
- {
- if (delta_E < 0.0) return true;
- return std::exp(-delta_E / T) > dist(rng);
- }
- };
- // 默认连续邻域生成策略
- template<typename State>
- struct DefaultNeighbor {
- double sigma = 1.0;
- State operator()(const State& current,
- double T,
- std::mt19937& rng) const
- {
- if constexpr (std::is_arithmetic_v<State>) {
- std::normal_distribution<double> dist(0.0, sigma * T);
- return static_cast<State>(current + dist(rng));
- }
- else if constexpr (detail::is_std_vector_v<State>) {
- using ValueType = typename State::value_type;
- static_assert(std::is_arithmetic_v<ValueType>,
- "vector value type must be arithmetic");
- std::normal_distribution<double> dist(0.0, sigma * T);
- State candidate = current;
- for (auto& v : candidate)
- v = static_cast<ValueType>(v + dist(rng));
- return candidate;
- }
- else {
- static_assert(sizeof(State) == 0, "No default neighbor for this State type");
- return current;
- }
- }
- };
- // 离散翻转邻域策略 (针对 vector<bool> 或 vector<int>)
- template<typename State>
- struct DiscreteFlipNeighbor {
- State operator()(const State& current,
- double T,
- std::mt19937& rng) const
- {
- static_assert(detail::is_std_vector_v<State>, "DiscreteFlipNeighbor requires std::vector");
- using ValueType = typename State::value_type;
- static_assert(
- std::is_same_v<ValueType, int> || std::is_same_v<ValueType, bool>,
- "DiscreteFlipNeighbor requires vector<int> or vector<bool>"
- );
- State candidate = current;
- std::uniform_int_distribution<std::size_t> dist(0, candidate.size() - 1);
- std::size_t idx = dist(rng);
- if constexpr (std::is_same_v<ValueType, bool>)
- candidate[idx] = !candidate[idx];
- else
- candidate[idx] = 1 - candidate[idx];
- return candidate;
- }
- };
- // 边界约束策略 (Box Constraint)
- template<typename State>
- class BoxConstraintPolicy {
- public:
- using ValueType = std::conditional_t<
- std::is_arithmetic_v<State>,
- State,
- typename State::value_type>;
- BoxConstraintPolicy(ValueType lower, ValueType upper)
- : lower_(lower), upper_(upper) {}
- void apply(State& state) const noexcept {
- if constexpr (std::is_arithmetic_v<State>) {
- state = std::clamp(state, lower_, upper_);
- }
- else {
- for (auto& v : state)
- v = std::clamp(v, lower_, upper_);
- }
- }
- private:
- ValueType lower_;
- ValueType upper_;
- };
- } // namespace sa
- #endif // SA_POLICIES_HPP
[code]#ifndef SA_DETAIL_SOLVER_HPP#define SA_DETAIL_SOLVER_HPP#include "../params.hpp"#include #include #include namespace sa::detail { template< typename State, typename EnergyFunc, typename NeighborFunc, typename CoolingPolicy, typename AcceptancePolicy, typename ConstraintPolicy > class Solver { public: Solver(Params params, EnergyFunc energy, NeighborFunc neighbor, CoolingPolicy cooling, AcceptancePolicy acceptance, ConstraintPolicy constraint) : params_(params), energy_(energy), neighbor_(neighbor), cooling_(cooling), acceptance_(acceptance), constraint_(constraint), dist_(0.0, 1.0) { validate_params(); if (params_.seed == 0) { std::random_device rd; rng_ = std::mt19937(rd()); } else { rng_ = std::mt19937(params_.seed); } } std::pair solve(const State& initial_state) { State current = initial_state; double current_energy = energy_(current); State best = current; double best_energy = current_energy; double T = params_.initial_temp; std::size_t total_iters = 0; while (T > params_.final_temp && total_iters < params_.max_total_iters) { for (std::size_t i = 0; i < params_.iter_per_temp && total_iters < params_.max_total_iters; ++i, ++total_iters) { State candidate = neighbor_(current, T, rng_); // 编译期判断是否存在约束策略 if constexpr (!std::is_same_v) { constraint_.apply(candidate); } double candidate_energy = energy_(candidate); double delta = candidate_energy - current_energy; if (acceptance_(delta, T, rng_, dist_)) { current = std::move(candidate); current_energy = candidate_energy; if (current_energy < best_energy) { best = current; best_energy = current_energy; } } } T = cooling_(T, params_); } return {std::move(best), best_energy}; } private: void validate_params() { if (params_.initial_temp |