经过前面的学习,Flink 的几个核心概念相关的源码实现我们已经了解了。本文我们来梳理 Task 的数据交互相关的源码。
数据输出
话不多说,我们直接进入正题。首先来看 Task 的数据输出,在进入流程之前,我们先介绍几个基本概念。
基本概念
- RecordWriterOutput:它是 Output 接口的一个具体实现类,底层使用 RecordWriter 来发送数据。
- RecordWriter:数据写入的执行者,负责将数据写到 ResultPartition。
- ResultPartition 和 ResultSubpartition:ResultPartition 是 ExecutionGraph 中一个节点的输出结果,下游的每个需要从当前 ResultPartition 消费数据的 Task 都会有一个 ResultSubpartition。
- ChannelSelector:用来决定一个 Record 要被写到哪个 Subpartition 中。
- LocalBufferPool:用来管理 Buffer 的缓冲池。在介绍反压的原理时,我们提到过。
对这些基本概念有了一定的了解之后,我们来看数据输出的具体流程。
执行流程
我们以 map 为例,看一下数据的输出过程。
在 StreamMap.processElement 方法中,调用完 map 方法之后,就会调用 output.collect 方法将数据输出,这里的 output 就是 RecordWriterOutput。在 RecordWriterOutput 中,会调用 RecordWriter 的 emit 方法。- private <X> void pushToRecordWriter(StreamRecord<X> record) {
- serializationDelegate.setInstance(record);
- try {
- recordWriter.emit(serializationDelegate);
- } catch (IOException e) {
- throw new UncheckedIOException(e.getMessage(), e);
- }
- }
接下来就是调用 BufferWritingResultPartition.emitRecord 来写入数据。- public void emitRecord(ByteBuffer record, int targetSubpartition) throws IOException {
- totalWrittenBytes += record.remaining();
- BufferBuilder buffer = appendUnicastDataForNewRecord(record, targetSubpartition);
- while (record.hasRemaining()) {
- // full buffer, partial record
- finishUnicastBufferBuilder(targetSubpartition);
- buffer = appendUnicastDataForRecordContinuation(record, targetSubpartition);
- }
- if (buffer.isFull()) {
- // full buffer, full record
- finishUnicastBufferBuilder(targetSubpartition);
- }
- // partial buffer, full record
- }
- private MemorySegment requestMemorySegment(int targetChannel) {
- MemorySegment segment = null;
- synchronized (availableMemorySegments) {
- checkDestroyed();
- if (!availableMemorySegments.isEmpty()) {
- segment = availableMemorySegments.poll();
- } else if (isRequestedSizeReached()) {
- // Only when the buffer request reaches the upper limit(i.e. current pool size),
- // requests an overdraft buffer.
- segment = requestOverdraftMemorySegmentFromGlobal();
- }
- if (segment == null) {
- return null;
- }
- if (targetChannel != UNKNOWN_CHANNEL) {
- if (++subpartitionBuffersCount[targetChannel] == maxBuffersPerChannel) {
- unavailableSubpartitionsCount++;
- }
- }
- checkAndUpdateAvailability();
- }
- return segment;
- }
有了可用的 buffer 之后,就会调用 addToSubpartition,最终数据存储在 PipelinedSubpartition 的 buffers 队列中。- private void addToSubpartition(
- BufferBuilder buffer,
- int targetSubpartition,
- int partialRecordLength,
- int minDesirableBufferSize)
- throws IOException {
- int desirableBufferSize =
- subpartitions[targetSubpartition].add(
- buffer.createBufferConsumerFromBeginning(), partialRecordLength);
- resizeBuffer(buffer, desirableBufferSize, minDesirableBufferSize);
- }
看完了数据输出的过程之后,我们再来看一下数据输入的过程。首先还是了解几个基本概念。
基本概念
- InputGate:InputGate 是对输入的封装,与 JobGraph 中的 JobEdge 一一对应,每个 InputGate 消费上游一个或多个 Resultpartition。
- InputChannel:InputChannel 是和 ExecutionGraph 中的 ExecutionEdge 一一对应的。每个 InputChannel 接收一个 ResultSubpartition 的输出,InputChannel 主要关注 LocalInputChannel 和 RemoteInputChannel 两种实现。
执行流程
了解了具体概念之后,我们再看数据输入的具体流程。
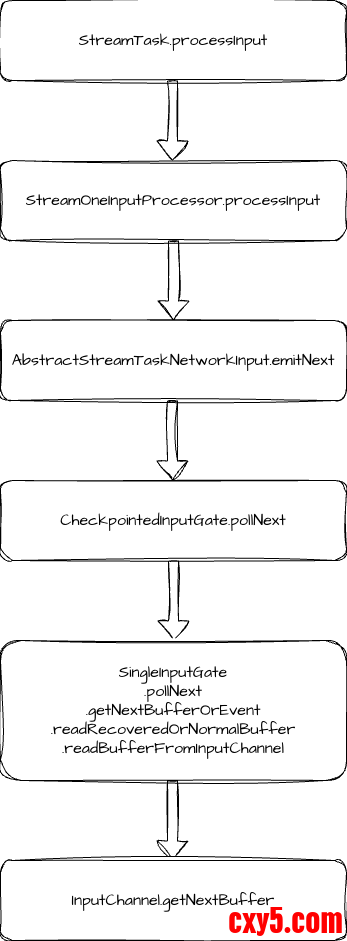
数据输入的入口是 StreamTask.processInput 方法,这个方法中主要是调用 inputProcessor.processInput 方法,我们以 StreamOneInputProcessor 为例。这个方法就是调用 input.emitNext 方法。- public DataInputStatus emitNext(DataOutput<T> output) throws Exception {
- while (true) {
- // get the stream element from the deserializer
- if (currentRecordDeserializer != null) {
- RecordDeserializer.DeserializationResult result;
- try {
- result = currentRecordDeserializer.getNextRecord(deserializationDelegate);
- } catch (IOException e) {
- throw new IOException(
- String.format("Can't get next record for channel %s", lastChannel), e);
- }
- if (result.isBufferConsumed()) {
- currentRecordDeserializer = null;
- }
- if (result.isFullRecord()) {
- final boolean breakBatchEmitting =
- processElement(deserializationDelegate.getInstance(), output);
- if (canEmitBatchOfRecords.check() && !breakBatchEmitting) {
- continue;
- }
- return DataInputStatus.MORE_AVAILABLE;
- }
- }
- Optional<BufferOrEvent> bufferOrEvent = checkpointedInputGate.pollNext();
- if (bufferOrEvent.isPresent()) {
- // return to the mailbox after receiving a checkpoint barrier to avoid processing of
- // data after the barrier before checkpoint is performed for unaligned checkpoint
- // mode
- if (bufferOrEvent.get().isBuffer()) {
- processBuffer(bufferOrEvent.get());
- } else {
- DataInputStatus status = processEvent(bufferOrEvent.get(), output);
- if (status == DataInputStatus.MORE_AVAILABLE && canEmitBatchOfRecords.check()) {
- continue;
- }
- return status;
- }
- } else {
- if (checkpointedInputGate.isFinished()) {
- checkState(
- checkpointedInputGate.getAvailableFuture().isDone(),
- "Finished BarrierHandler should be available");
- return DataInputStatus.END_OF_INPUT;
- }
- return DataInputStatus.NOTHING_AVAILABLE;
- }
- }
- }
我们以 SingleInputGate 为例看 InputGate 的 pollNext 方法。它的内部调用链路可用一直追踪到 readBufferFromInputChannel 方法,这个方法内会调用 inputChannel.getNextBuffer,这里交给 InputChannel 来具体执行数据读取。- public Optional<BufferAndAvailability> getNextBuffer() throws IOException {
- checkError();
- if (!toBeConsumedBuffers.isEmpty()) {
- return getBufferAndAvailability(toBeConsumedBuffers.removeFirst());
- }
- ResultSubpartitionView subpartitionView = this.subpartitionView;
- if (subpartitionView == null) {
- // There is a possible race condition between writing a EndOfPartitionEvent (1) and
- // flushing (3) the Local
- // channel on the sender side, and reading EndOfPartitionEvent (2) and processing flush
- // notification (4). When
- // they happen in that order (1 - 2 - 3 - 4), flush notification can re-enqueue
- // LocalInputChannel after (or
- // during) it was released during reading the EndOfPartitionEvent (2).
- if (isReleased) {
- return Optional.empty();
- }
- // this can happen if the request for the partition was triggered asynchronously
- // by the time trigger
- // would be good to avoid that, by guaranteeing that the requestPartition() and
- // getNextBuffer() always come from the same thread
- // we could do that by letting the timer insert a special "requesting channel" into the
- // input gate's queue
- subpartitionView = checkAndWaitForSubpartitionView();
- }
- BufferAndBacklog next = subpartitionView.getNextBuffer();
- // ignore the empty buffer directly
- while (next != null && next.buffer().readableBytes() == 0) {
- next.buffer().recycleBuffer();
- next = subpartitionView.getNextBuffer();
- numBuffersIn.inc();
- }
- if (next == null) {
- if (subpartitionView.isReleased()) {
- throw new CancelTaskException(
- "Consumed partition " + subpartitionView + " has been released.");
- } else {
- return Optional.empty();
- }
- }
- Buffer buffer = next.buffer();
- if (buffer instanceof FullyFilledBuffer) {
- List<Buffer> partialBuffers = ((FullyFilledBuffer) buffer).getPartialBuffers();
- int seq = next.getSequenceNumber();
- for (Buffer partialBuffer : partialBuffers) {
- toBeConsumedBuffers.add(
- new BufferAndBacklog(
- partialBuffer,
- next.buffersInBacklog(),
- buffer.getDataType(),
- seq++));
- }
- return getBufferAndAvailability(toBeConsumedBuffers.removeFirst());
- }
- return getBufferAndAvailability(next);
- }
RemoteInputChannel 则需要从 receivedBuffers 中读取数据,这个队列的数据就是消费上游数据后保存的。
至此,Flink 中 Task 的数据输入和输出过程的源码就梳理完了,更加底层的 Netty 相关代码我们在后面继续梳理。
总结
最后简单总结一下,本文我们梳理了 Task 的数据输出和输入的过程。输出过程主要是利用 RecordWriter 将数据写入到 Buffer 中,输入过程则是利用 InputChannel 从 Buffer 消费的过程。如果你的 Flink 任务数据量特别大,并且没什么复杂的逻辑,可以考虑适当调整 localBufferPool 的大小来调优任务的吞吐。
来源:程序园用户自行投稿发布,如果侵权,请联系站长删除
免责声明:如果侵犯了您的权益,请联系站长,我们会及时删除侵权内容,谢谢合作! |