|
本文内容包含所有的Crypto,三道PIoTS,两道Re以及两个系列的Misc题,主要用于记录 Crypto高位攻击完全用不到pq高位信息,因为d大概是n的0.2544次幂,所以直接套boneh donfee板子就可 [code]# SageMath 9.3
N = 28384198625234311024055591508760545859772557962616705058087134570313766078246339432810722251075770426155260882976548948745855775802466082136886198916308950895091350291804323083377746723426585662829956721593008069417593656058519847917141571157423337000995823498275338699783892359735051369928648561714630161425631668045643208548745557419257154201912621422125784538013535319473974771074731705230991582524865280419594116357454200441743555890216903447536600103202560201259871803992219002685757605178878578265090068993111854329728311196716695934142083541791762952464173221834117578210442075243829228771641151482461878395681
e = 24233198590433138929759046268361507704173924810200652679220620112938468106193887274039561623781677698718659545011949842007599587857513820908529013019054134965026341908641820214813864848590705039503962393544485942577593170832200318338048424938687583902593193451991009036073079376645787351773806712023712043915544661222738699918976674231029998684765476662313863475966304161444465282825845046504385175046765187829943107254178661647191288636247051016225997643316505985860750972663378492448313338846037936997542245777268091759458108263910160659565995588095034641162401363842335174968680271594738396192872825937509377247217
c = 940844774044002760041224401562703091111426466612866082339966140841639939444648025078973826624076043358296937037021610358779157680065548800768654725751103021962957103161713314365598234258437018412919647354775780700585758075623352776449216395723630660676425946215835561424716152933938854890964273887565373627808873987131623770696128641766795559659984456300489545944324461938795805156161909329750290251725440271617055330398638953715159135274381585663770711778978803710571670536163056904818086237979881559953073139720433782186818163069926281641109314202702006420384137994982480163260679548223758917067813649186512456317
"""
Setting debug to true will display more informations
about the lattice, the bounds, the vectors...
"""
debug = False
"""
Setting strict to true will stop the algorithm (and
return (-1, -1)) if we don't have a correct
upperbound on the determinant. Note that this
doesn't necesseraly mean that no solutions
will be found since the theoretical upperbound is
usualy far away from actual results. That is why
you should probably use `strict = False`
"""
strict = False
"""
This is experimental, but has provided remarkable results
so far. It tries to reduce the lattice as much as it can
while keeping its efficiency. I see no reason not to use
this option, but if things don't work, you should try
disabling it
"""
helpful_only = True
dimension_min = 7 # stop removing if lattice reaches that dimension
############################################
# Functions
##########################################
# display stats on helpful vectors
def helpful_vectors(BB, modulus):
nothelpful = 0
for ii in range(BB.dimensions()[0]):
if BB[ii, ii] >= modulus:
nothelpful += 1
print(nothelpful, "/", BB.dimensions()[0], " vectors are not helpful")
# display matrix picture with 0 and X
def matrix_overview(BB, bound):
for ii in range(BB.dimensions()[0]):
a = ('%02d ' % ii)
for jj in range(BB.dimensions()[1]):
a += '0' if BB[ii, jj] == 0 else 'X'
if BB.dimensions()[0] < 60:
a += ' '
if BB[ii, ii] >= bound:
a += '~'
print(a)
# tries to remove unhelpful vectors
# we start at current = n-1 (last vector)
def remove_unhelpful(BB, monomials, bound, current):
# end of our recursive function
if current == -1 or BB.dimensions()[0] <= dimension_min:
return BB
# we start by checking from the end
for ii in range(current, -1, -1):
# if it is unhelpful:
if BB[ii, ii] >= bound:
affected_vectors = 0
affected_vector_index = 0
# let's check if it affects other vectors
for jj in range(ii + 1, BB.dimensions()[0]):
# if another vector is affected:
# we increase the count
if BB[jj, ii] != 0:
affected_vectors += 1
affected_vector_index = jj
# level:0
# if no other vectors end up affected
# we remove it
if affected_vectors == 0:
# print("* removing unhelpful vector", ii)
BB = BB.delete_columns([ii])
BB = BB.delete_rows([ii])
monomials.pop(ii)
BB = remove_unhelpful(BB, monomials, bound, ii - 1)
return BB
# level:1
# if just one was affected we check
# if it is affecting someone else
elif affected_vectors == 1:
affected_deeper = True
for kk in range(affected_vector_index + 1, BB.dimensions()[0]):
# if it is affecting even one vector
# we give up on this one
if BB[kk, affected_vector_index] != 0:
affected_deeper = False
# remove both it if no other vector was affected and
# this helpful vector is not helpful enough
# compared to our unhelpful one
if affected_deeper and abs(bound - BB[affected_vector_index, affected_vector_index]) < abs(
bound - BB[ii, ii]):
# print("* removing unhelpful vectors", ii, "and", affected_vector_index)
BB = BB.delete_columns([affected_vector_index, ii])
BB = BB.delete_rows([affected_vector_index, ii])
monomials.pop(affected_vector_index)
monomials.pop(ii)
BB = remove_unhelpful(BB, monomials, bound, ii - 1)
return BB
# nothing happened
return BB
"""
Returns:
* 0,0 if it fails
* -1,-1 if `strict=true`, and determinant doesn't bound
* x0,y0 the solutions of `pol`
"""
def boneh_durfee(pol, modulus, mm, tt, XX, YY):
"""
Boneh and Durfee revisited by Herrmann and May
finds a solution if:
* d < N^delta
* |x| < e^delta
* |y| < e^0.5
whenever delta < 1 - sqrt(2)/2 ~ 0.292
"""
# substitution (Herrman and May)
PR.[/code]
EzAESkey、IV、c均已知,直接AES解密即可,然后再套一层MD5,带上flag{}壳提交 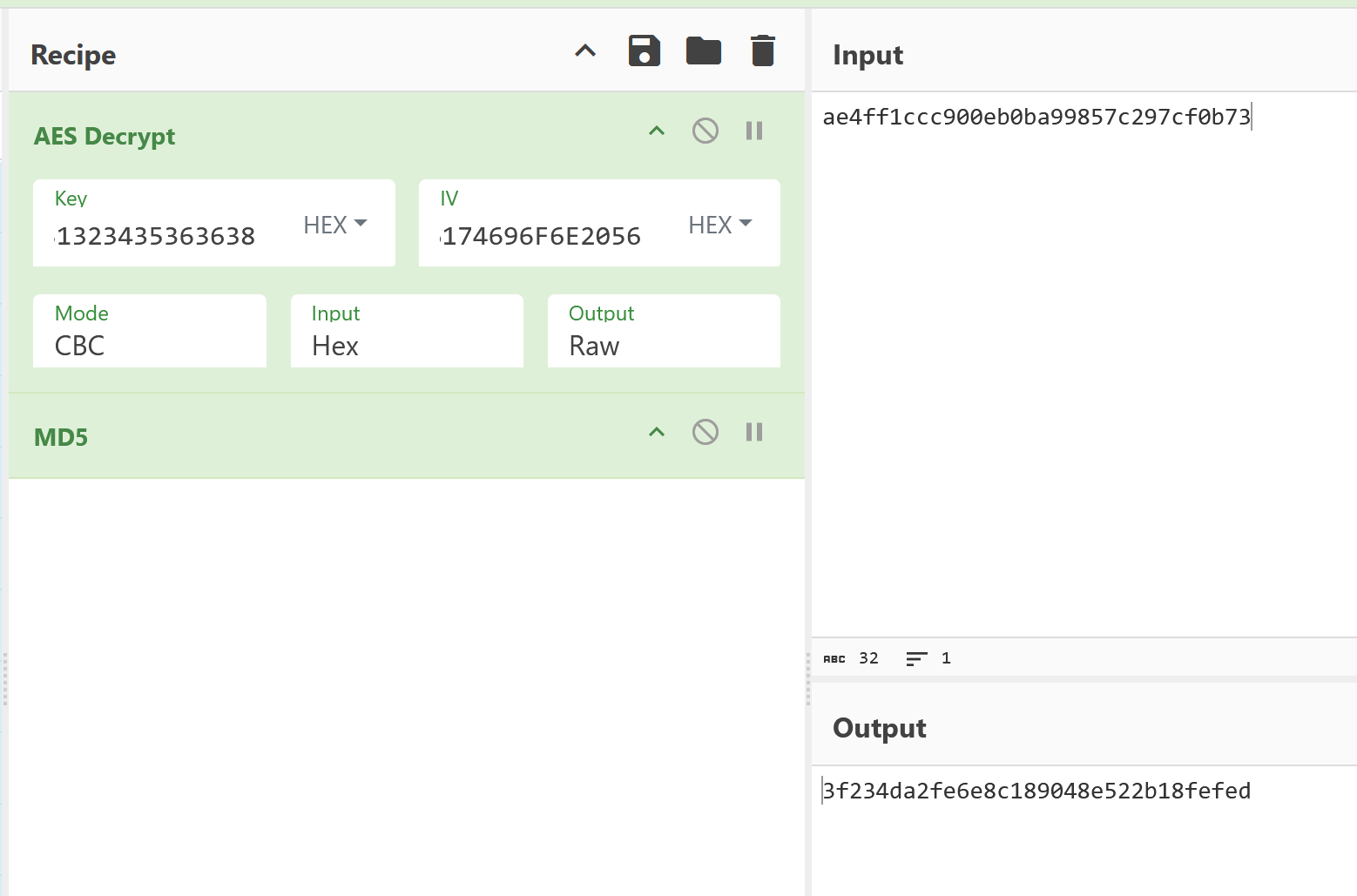 trod[code]import sys
def Sn(i):
s = ''
while i != 0:
digit = i & 0xff
i >>= 8
s += chr(digit)
return s
def In(s):
val = 0
for i in range(len(s)):
digit = ord(s[len(s) - i - 1])
val <<= 8
val |= digit
return val
def egcd(a, b):
if a == 0:
return b, 0, 1
else:
g, y, x = egcd(b % a, a)
return g, x - (b // a) * y, y
def mod_inv(a, p):
a %= p
g, x, y = egcd(a, p)
if g != 1:
raise Exception('No inverse exists')
else:
return x % p
def add(a, b, p):
if b == -1: return a
if a == -1: return b
x1, y1 = a
x2, y2 = b
# 分母
denom = (x1 + x2 - y1 - y2 - 1) % p
inv_denom = mod_inv(denom, p)
x3 = ((x1 * x2 - x1 * y2 - x2 * y1 + 2 * y1 * y2) * inv_denom) % p
y3 = ((y1 * y2) * inv_denom) % p
return x3, y3
def double_add(a, p):
return add(a, a, p)
def mod_mul(m, g, p):
r = -1
while m != 0:
if m & 1:
r = add(r, g, p)
m >>= 1
g = double_add(g, p)
return r
# --- 破解逻辑 ---
from sympy.ntheory import discrete_log
p = 518176062457782304884612410952519332834134329945067733347561865398388593
g = (36787147675581394808139907493983017478037802710811666907537030656, 9196786918895348702034976873495754369509450677702916726884257664)
A = (123420721694594649929479399223574107534344333995718594245237838243095171, 441474954859299544474995920494435026572932663211423760492509380991644019)
B = (201033191494423227078517457992052009778645182262306784843547224098182904, 218648529653244920425405172206343059964354475824649267929238496666580596)
encrypted_message = 100093982037856112608548215034731454533357581263010216959659834987333181487918721876307552567021052798183868853477600221794005089397754541179893146978
def map_point(P, p):
"""
同态映射函数 phi(x, y) = (x - y - 1) / (x - y) mod p
"""
x, y = P
u = (x - y) % p
# phi = 1 - 1/u = (u-1)/u
num = (u - 1) % p
den = mod_inv(u, p)
return (num * den) % p
def solve():
print("[*] Calculating mapped values...")
val_g = map_point(g, p)
val_A = map_point(A, p)
print("[*] Solving Discrete Logarithm (this might take a moment depending on p-1 smoothness)...")
# 求解: val_g ^ a = val_A (mod p)
# sympy.discrete_log 能够自动处理 Pohlig-Hellman 算法
aliceSecret = discrete_log(p, val_A, val_g)
print(f"[+] Found Alice's Secret: {aliceSecret}")
print("[*] Calculating Shared Secret...")
# S = aliceSecret * B (using custom group mul)
S = mod_mul(aliceSecret, B, p)
# 根据题目逻辑计算 masterSecret
masterSecret = (S[0] * S[1]) # 注意这里是普通乘法,不是模 p 乘法,根据题目逻辑 masterSecret = aliceMS[0] * aliceMS[1]
print("[*] Decrypting...")
decrypted_int = encrypted_message ^^ masterSecret
flag = Sn(decrypted_int)
print(f"\n[SUCCESS] Flag: {flag}")
if __name__ == '__main__':
solve()
'''
[*] Calculating mapped values...
[*] Solving Discrete Logarithm (this might take a moment depending on p-1 smoothness)...
[+] Found Alice's Secret: 5893410662100511584121728146593578127178145692816888878
[*] Calculating Shared Secret...
[*] Decrypting...
[SUCCESS] Flag: flag{Who_has_the_computer_organization_principle_in_the_exam?}
'''
[/code]
创造lcg一开始没想到一个点,flag并不是由反推的初始的LCG状态列表得出来的,而是由当前状态再经过一次lcg变换得到的下一状态得出来的。通过打印并观察每一轮对应的假的flag看出来的,然后就只需要对当前状态进行一次lcg变化然后读出对应flag即可 [code]from Crypto.Util.number import long_to_bytes, inverse
final_lcg = [
531812496965714475754459274425954913,
573493247306997567791036597408132959,
531874692922906583591521900672740733
]
a = 678292774844628690689951
b = 799218428050845578943269
c = 871991670671866736323531
p = 226554022535584634512578046463759712133
current_state = list(final_lcg)
new_state = (a*current_state[0] + b*current_state[1] + c*current_state[2]) % p
current_state = current_state[1:] + [new_state]
val_nplus1 = current_state[0]
val_nplus2 = current_state[1]
val_nplus3 = current_state[2]
inv_a = inverse(a, p)
val_n = (inv_a * (val_nplus3 - b * val_nplus1 - c * val_nplus2)) % p
current_state = [val_n] + current_state[:2]
flag_bytes = b""
for part in current_state:
flag_bytes += long_to_bytes(part)
print(flag_bytes.decode())
# flag{try_to_transform_it_into_formulaic_form}
[/code]
xiaoji的RSA[code]from Crypto.Util.number import *
from math import gcd
c = 18062960292926203405106631570645792887346762710596094595946201638145269792362432970619678514073768330282072122297774770846723026262793638145140252714036118255298935496782643261099997757452005888950084317572578983859160308143219449311014720216597693717833093096186064214815571678655104145532183363580096161113659794514705540535423432576540755810113817779577012494191762397204056012915596163266097092210799790994886142736276356044755057247863118120000651380079123033610186723297866795705886993017274323290850712391555552018597217459748407996232225971214252337750534257640641166056960137653051788480104937847471213865531
leak = 29786109562795434767286575222202920392934698151772733519827029723076564127577506924725472620552207928305324807071633980845799428305323747287497587012814817694240321762385052643719779704776885137653915759833442842418374852111545817139388092965791383085268376283252367393215830021523854878152740193684532064211244526477475872824124551317767515936013314015487953976823909663377712672258700701049790904432754196590520755614551428222850284265995888579989169357385240073615572407415594868320441237551194011351100321407974631166974196395240849462596136681294133772802147270429624576958515766511950802469230517874955000694776
h1 = 14598570770570369251044298637863318854969244053819114954671895416691350802920687681668270301378543649113252159681469894140327953343981428435557763783575047421073785093934100988516182011757805151301552786226747639175213248064364104458391503594386384710007637410647669428289271030281975860741433987188926890687769189330536656978907095466736760156091550669274865538908426382007469741745093518762985240171234021436305408209014615992584706412209748494302146308826117702351113891442300797965409831595569786933763773967575744129781374727612526423706127336276048951135368854093017991855415497273999713365969103371554004824509
h2 = 11655430400126708521266628893465012008156070100550313215125940102411494976112918677189030755406554269846801368688286768397687408859238412058773272768466345174217960738213084397497134648104645110774595383007722678343723326165844773931623583737649558732929341710652376370393000666923877685083880991816166675473675993119565288119886891401337292448811477124318462203416303782364411201690259713617106545395093938159021072322598644028525378190756212177234492649667270787158675885995463312527798325191816554894434526912762675422186788558909636033206644624947398671285555871818986699430277747968998624440765160214625508302582
n = 16117539256891249484718413429700173002583084988861340273782389608188420881800342876872775121756821301056788500260045796850939585388076522939011021777251658702207624594144564384121357888401608404641571728859619754015070281985119363898471820577703197516678288716301039869441770173970562352919565912788016889342101896134309321994797037369608180360632790282197647969119609543804552490560372790883065970972189091831856508916272396614853136857081227250153104695845022919856333090412792344985816893032033703744649648621089458783293225651830841418574525258165458710362104364949367148707705685722700758399918195168711661909001
# solve linear system for c1,c2:
c1 = (c + leak) // 3
c2 = c - c1
K = 7717*8859
a = pow(h1, 8859, n)
b = pow(h2, 7717, n)
t2024 = pow(2024, K, n)
t2025 = pow(2025, K, n)
X = (a * t2025 - b * t2024) % n
g = gcd(X, n)
p = g
q = n // p
e = 0x10001
phi = (p-1)*(q-1)
d = inverse(e, phi)
m1 = pow(c1, d, n)
m2 = pow(c2, d, n)
print((long_to_bytes(m1)+long_to_bytes(m2)).decode())
# flag{fc08e137-5be9-4677-a1f5-4e640223df0e}
[/code]
渐增套娃cryisc题,通过观察,注意到本题涉及到qwerty坐标密码,具体来说,这个24292125,其中的22代表第二行第二列,经过验证flag拼在一起为24292125与题目一致,对三段密文开始解密,第一段结果为stepwise,第二段为nwlahycrxw,无意义单词,Rot枚举一下偏移量,发现为9时得到有意义文本encryption,第三段为nomziboc,Rot枚举偏移量为21时得到有意义文本strength,最后根据题目说明拼出flag为flag{stepwise encryption strength} PIoTS默认密钥漏洞xor题目提到数据使用了出厂未修改的默认全局链路密钥“ZigBeeAlliance09”,因此通信负载可被直接解密。将 payload 与该默认密钥循环 XOR 后,可在正确偏移3处还原出可读明文。最终明文中包含的字符串即为题目flag [code]data = open(r"E:\Downloads\zigbee_traffic.pcap","rb").read()
payload = data[0x28:]
key_hex = "5A6967426565416C6C69616E63653039".lower()
key = bytes.fromhex(key_hex)
def score_plain(b):
printable = 0
for c in b:
if 32 <= c <= 126:
printable += 1
return printable/len(b)
candidates = []
for s in range(len(payload)):
out = bytearray(payload) # full
for i in range(s,len(payload)):
out[i] ^= key[(i-s)%len(key)]
sc = score_plain(out[s:]) # only encrypted tail
candidates.append((sc,s,out))
sorted(candidates, reverse=True)[:10][:3]
cands=[]
for s in range(len(payload)):
out = bytearray(payload)
for i in range(s,len(payload)):
out[i] ^= key[(i-s)%len(key)]
sc = score_plain(out)
cands.append((sc,s,out))
if b'flag' in out:
print(out)
break
sorted(cands, reverse=True)[:10]
# bytearray(b'\x00\x08\x01SensorData: flag{thepolarinthezigbee}')
[/code]
点击挑战首先解包 APK,使用 jadx 查看代码,在 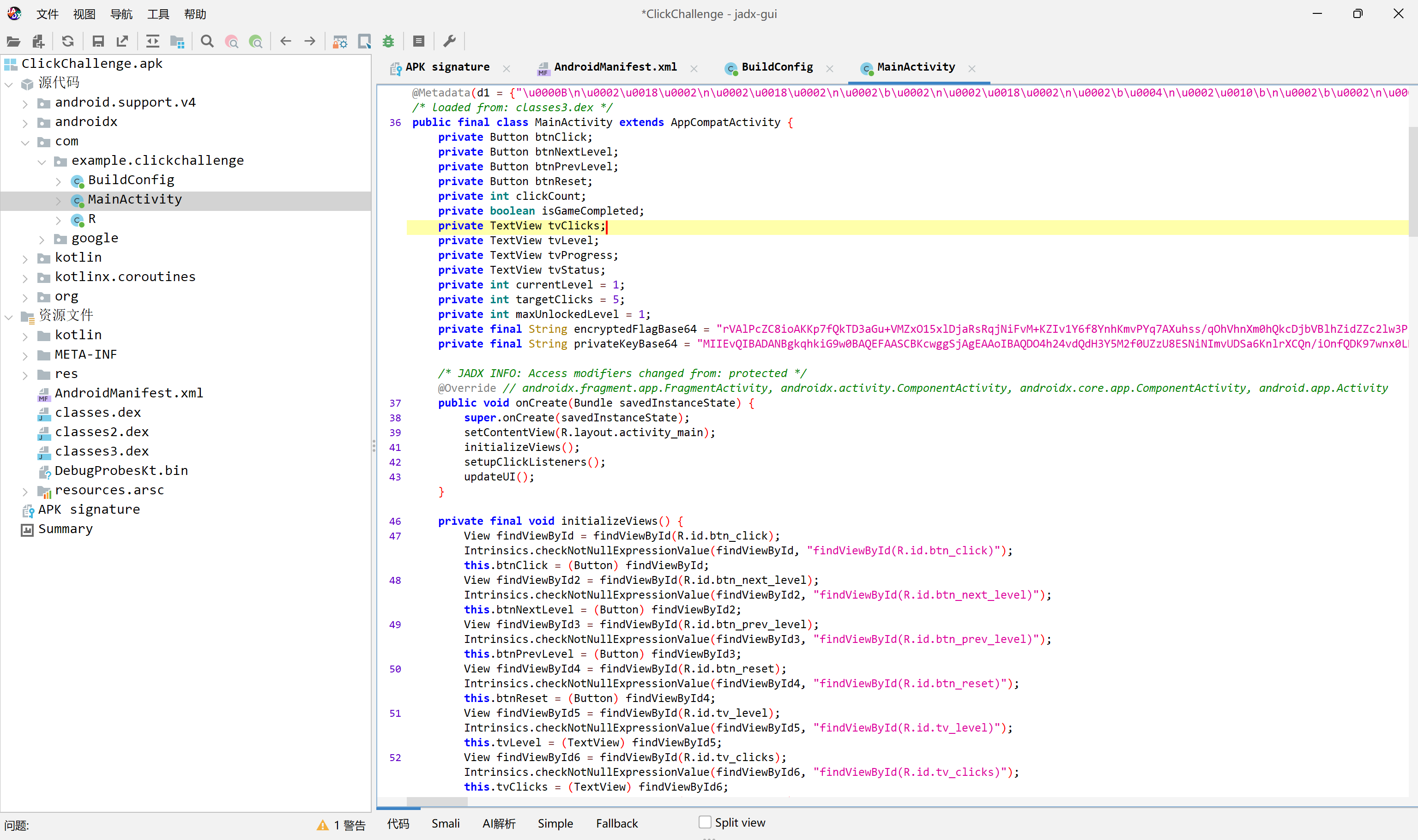 import base64
from Crypto.PublicKey import RSA
from Crypto.Cipher import PKCS1_v1_5
def main():
# APK 中提取出的 Base64 私钥
key_b64 = """
MIIEvQIBADANBgkqhkiG9w0BAQEFAASCBKcwggSjAgEAAoIBAQDO4h24vdQdH3Y5M2f0UZzU8ESNiNImvUDSa6KnlrXCQn/iOnfQDK97wnx0LDibNlMAE50AizHGXwlWClBqtMohObbiFgZrpONbw1Xyg6sGVPPjDHpqgZkV7iXpAnQdphkeEkp2YVYWPaAwFj+lIQl9IuyW1uaGqYKcAzI4xd9juzA1h9wZjXSVyAo77q/HbNVgM1RFw0zQuUJ8qV1rAZv1zrkv7bRO4O4EC00fxzcvbOdos8WwjKvBwSWI52oJEQ6rhYk471o9YkE6pWxuWWORnjLmmI/Eb66BrVUwLZSyTxtUWNrMqyOmtNlkH6H9HL3MrnrPLRiu6m2BrsOnPDmrAgMBAAECggEAIyqEata5q4mhiu+WCA2nXvrIbFaJglRBJINvTpVrp+2t10KhAxhk6+CPTyAFLzz4ttaepW0DtPiKmbl/GeRJR4SL9bpQtRN+Iib+AQ8ojxb5rep9FIWbBANLJmRoYHHPazEovx6kh3tKM2JUxzjqZ/77wFgfL1y4+tQAQW5BHq5wsnKgW5/kysZf1tNhBvyNCowJF0JxisoGvx5nx63J+d+TAM0XPpQ8RBVFjoR3W2odWdpeAmbMl1Aa4ZihcskBbp4EqYr1QZYGuONzLBLaqtwu+E+uC0JPU3dxy9te3Yjs33Dd41gcg8v6HnTrNFntsfR9TojLmEL5N8q+DWvKgQKBgQDlxYmlfefj+b5+FOuokJWX3ioYhFxM4OVF2WkTirAcydm+b7Teacmc3YL9xr0If+88trjb7b8BXCwiterpFi0Pax/z5u7ZIJ8BA1MwybC0CIBzy2i0tMU0qCPCaMYkrEHjKBrYmSIXAy3jqyZ4V9QMkO4pcJoEPNCSyBPr3cZVewKBgQDmf7oglk890b0CVdFNYzPN2Du01OZ5y7aJbzKGlo/H+xx8Qkm/eUeaIOPTWemZaJYCHOQHKHMN/Zp50qE/g7OkQifrvHSJR+PgLv+YN/Y0Our2zIiY5wdZRNZj6k6l9eDbsR65lDC3bhwahuYBQ1yvHzSdaRjeMCJ2Agod6z69kQKBgCrlTQQ7VC5ocprBNxmaHINks4EuPLkRh1wZ8Zb3XleRi3gVDLQ1FbGWXR0ZnDLZB4XTKwHMCcusNIUqZzeqrzDgs+9p3o9kmqqqvz4teTKzH5/+ioap9OMWvM5PlyZDjm1lEFX9iLK5IjkNu7nd07Wg3QWZgvdljx7IAYgYOC2/AoGADXeG82J0zMLVTS6gZOoX2733dxA9Sv5o8sypYg2n5uI3/taMooA+e7XSOcX2DP18TjFL7VMirb2UaeuxehmCxGUNGgvPrzmhCbcVPdp/KvwKQFMg4/YTitanw/yrjay4730As40B76WiRLZ+97Hs11p2Y4ABcPHVAZoK50aYStECgYEAxktu0YJ2By/rRPB1kAkttSb6PvEAuIwuwUFmttYiNuO8dQktpLjCoi62eyUzPxHWcY0Hxi92IAqfS697e9skEMKrepRZ6ysAkKjOMaJhVAwA+XAdRhaPimy4miDFa5dSFPxcc0JwfCAXkX2C/jjYc9s7t4jOMDnYhGszlzGdjNU=
""".strip()
# APK 中提取出的 Base64 密文
cipher_b64 = """
rVAlPcZC8ioAKKp7fQkTD3aGu+VMZxO15xlDjaRsRqjNiFvM+KZIv1Y6f8YnhKmvPYq7AXuhss/qOhVhnXm0hQkcDjbVBlhZidZZc2lw3PIc1mphUVgj+rd1hu3xwDY8Gsh1CNEx0H878B93T+OVshWh6IygFi6VFHEnfYOh99vPcA6MbeaRFMb4ZhWvr122X0/dxsrP1KXlQEWcnLXtPpbIB7aXjwHb1nqUNaD4EaDqNoouF+CxA4YOt4Oh8sHqh8BtNsD2khSrz6rS5mi7DRff4A4RxRvW4SVU0p7z5v6/KXgdhPe7df9k9duKDUgJ8BooPbMJnG/RuqljK3MR3g==
""".strip()
# 解码并导入私钥
key_der = base64.b64decode(key_b64)
rsa_key = RSA.import_key(key_der)
# 初始化 PKCS1Padding 解密器
cipher = PKCS1_v1_5.new(rsa_key)
# 解密
ciphertext = base64.b64decode(cipher_b64)
plaintext = cipher.decrypt(ciphertext, None)
if plaintext is None:
print("解密失败,请检查数据。")
else:
print(plaintext.decode())
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
# flag{8baf11bb16c9c14a5577e3ed0658bed3}
[/code]
ESP32_AP非预期,直接在附件中搜索 NFC水卡首先理解题意,题目所要求的应该是第 1 张卡中“总金额+对应校验位”所在扇区的扇区内容 ,首先观察两张原卡的结构,显然只有第 0 扇区和第 2 扇区中数据较多。题目明确指出金额和校验位在同一扇区,因而可以确定为第二扇区。对比观察可以发现第 1 行和第 3 行完全对称,明显是金额块和其备份,特征包括前 9 个字节全是 多提交验证几次,尝试不同的提交格式,得到正确的结果为如下字段,flag为flag{46FEED7D708C39B9C843768F0559F1C0} [code]00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 FF F6 34 00 09 CB FD
58 00 00 01 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 59
00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 FF F6 34 00 09 CB FD
12 63 22 33 53 13 FF 07 80 69 12 63 22 33 53 13
[/code]
Re练习1先从二进制中提取到伪装的模板串 templ = b"flag{PbkD7j4x|8Wz::z_01}"
def transform(t):
t = list(t)
out = ['\x00']*0x32
idx = 0
# first 5
for b4 in range(5):
out[idx] = chr(t[b4])
idx+=1
# next 7 XOR 7
for d4 in range(7):
ch = t[idx]
out[idx] = chr(ch ^ 0x7)
idx += 1
# next 7 XOR 8
for f4 in range(7):
ch = t[idx]
out[idx] = chr(ch ^ 0x8)
idx+=1
# remaining until idx reaches len(t)
while idx < len(t):
out[idx] = chr(t[idx])
idx+=1
out[idx] = '\0'
return "".join(out[:idx])
print(transform(templ))
# flag{WelC0m3pt0_r22z_01}
[/code]
peek_stack程序要求输入中文口令“秘密口令2025”,若匹配则进入生成 flag 的函数。该函数会先输出固定前缀“flag{”,然后将口令的 UTF-8 字节逐字节与 0x5A 异或并输出,最后添加“}”。因此只需提取口令字节并 XOR 0x5A,即可得到最终 flag [code]secret_utf8 = "秘密口令2025".encode("utf-8")
flag_hex_middle = ''.join(f"{b^0x5a:02x}" for b in secret_utf8)
print(f'flag{{{flag_hex_middle}}}')
# flag{bdfdc2bff5dcbfd5f9bee1fe686a686f}
[/code]
MiscSource of danger系列网站 IP 浏览器及版本 图片上写的内容 商品名/图片文字为 木马使用的库版本 木马窃取信息中的网站 URL 网站: http://192.168.27.15/source/ecshop/admin/privilege.php
用户名: admin
密码: ...
[/code]
题目要求完整url,所以 flag 填 Virtual_currency系列检材只用到了两个数据,一个是polar文件夹,一个是polarCTF.exe,只需要对这两个展开分析即可 虚拟货币的名称 前端页面 index.html 的标题为“Polar币交易平台”,且余额显示单位为 “POL”。服务端区块链逻辑中未定义其他币名,因此平台所使用的虚拟货币即为 Polar币。因而虚拟货币名称为 Polar币 黑客的地址 从日志分析可见,该地址频繁被查询余额并参与交易,是平台主要操作者使用的主账号。结合客户/中间账号行为分布可知,该地址对应题目所述的“黑客本人”。因而黑客地址为 9598f90b557fdf01558f9061c09195647f3ca9261264485319279e1da7a7ac48 黑客和客户使用的中间账号地址 logs 显示此地址先被客户端页面访问,又被黑客侧查询,是双方共同使用的账号。结合题意“黑客与客户交互的中转账户”,可确定这是中间账号。因而中间账号地址为 9004ddca99ff4aa70ef6cd27d2f3b81103c25d33c1384549a4f3bb0fdc035ef4 客户的 IP 从访问日志可见,192.168.192.129 进行页面登录、交易发送、手动挖矿等典型“前端用户”操作。与后台矿机(192.168.192.130)区分后,129 明显对应题目描述的“客户”。因而客户 IP 为 192.168.192.129 黑客植入的矿机木马是什么? 逆向 miner.py 显示木马直接将自身注册为 Windows 服务 “polarCTF”,作为后台挖矿程序运行。程序未释放其他挖矿文件,因此木马本体即为 EXE 本身。因而木马文件名为 polarCTF.exe 来源:程序园用户自行投稿发布,如果侵权,请联系站长删除 免责声明:如果侵犯了您的权益,请联系站长,我们会及时删除侵权内容,谢谢合作! |


3 硬核核心训练 “我们并非只是这副躯壳,别过分执着于皮囊表象。”—— 乔治・哈里森 作为一名痴迷功能性健身的爱好者,我一直渴望近距离观察人体内部的运转机制。所以几年前,当我的一位客户送给我《人体世界》展
个人电脑上的本地私有知识库解决方案:访答知识库深度解析 在信息爆炸的时代,如何有效管理和利用个人知识资产成为了许多专业人士面临的挑战。随着数据隐私意识的增强,越来越多的用户开始寻求既安全又高效的知识管